Do You Wake Up With a Wet Pillow? Find Out Why You Drool While You Sleep
Why You Might Drool in Your Sleep—and When to Worry
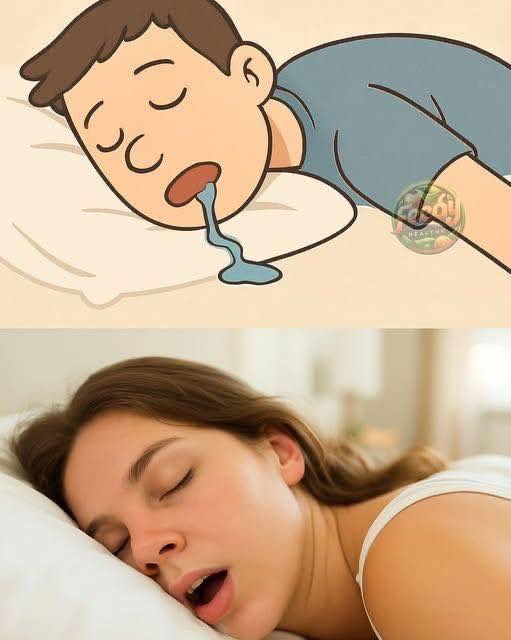
Waking up with a wet pillow might feel embarrassing, but drooling during sleep is actually quite common and usually harmless. For many people, it’s simply a natural part of the sleep cycle. However, understanding why it happens—and when it might signal a bigger issue—can help ease your mind or prompt you to take action if needed.
The Science Behind Sleep Drooling
When we enter deep sleep, especially during the REM (Rapid Eye Movement) stage, our bodies become deeply relaxed. This includes the muscles of the face, mouth, and jaw. As these muscles loosen, your mouth may fall slightly open. Normally, saliva is continuously produced and swallowed, even during sleep. But if your mouth is open, the saliva may instead escape and end up on your pillow.
This process is completely involuntary. It doesn’t mean you’re sleeping too deeply or poorly—on the contrary, it often means you’re in a restful stage of sleep. So in most cases, drooling is just a sign your body is fully at rest.
Your Sleep Position Matters
The way you sleep plays a major role in whether or not you drool. People who sleep on their side or stomach are far more likely to experience drooling because gravity encourages saliva to flow outward from the mouth. In contrast, those who sleep on their back often keep their mouths closed or swallow more frequently, which helps prevent saliva from leaking.
If drooling bothers you or happens often, simply changing your sleep position to lying on your back may be an effective fix.
When Breathing Through the Mouth Becomes the Culprit
Nasal congestion is another big contributor. When you have a cold, allergies, or a sinus infection, your nasal passages may be blocked, forcing you to breathe through your mouth. This not only dries out your mouth but can also lead to more drooling as your ability to swallow regularly is reduced during sleep.
Treating the root cause—such as using a decongestant, nasal strips, or allergy medication—can often reduce or eliminate drooling caused by mouth breathing.
When Drooling Could Point to a Health Problem
While occasional drooling is nothing to worry about, persistent or excessive drooling could indicate an underlying issue, especially if it’s accompanied by:
-
Chronic nasal congestion
-
Choking during sleep
-
Interrupted sleep
-
Difficulty swallowing
-
Snoring or gasping for air
In such cases, drooling might be linked to conditions like:
-
Sleep apnea – which affects your breathing during sleep and can increase mouth breathing and drooling.
-
Acid reflux or GERD – which may increase saliva production and lead to drooling.
-
Neurological disorders – such as Parkinson’s disease or the aftermath of a stroke, where muscle control is affected.
-
Dental issues – including tooth infections, gum problems, or poorly fitted dental appliances.
If you suspect any of these conditions, it’s a good idea to talk with a healthcare provider. A sleep study or further medical testing might be necessary.
Simple Tips to Reduce Drooling
For most people, small lifestyle changes can reduce or eliminate nighttime drooling:
-
Sleep on your back with your head slightly elevated.
-
Keep nasal passages clear using saline sprays or allergy treatments.
-
Practice good oral hygiene and visit your dentist regularly.
-
Stay hydrated—sometimes dry mouth can trigger excess saliva production later.
-
Avoid heavy meals or alcohol right before bed, as these can relax throat muscles.
Final Thoughts
Drooling in your sleep isn’t something to be ashamed of—it happens to people of all ages and health conditions. Often, it’s just a quirk of how your body behaves during rest. But if it becomes frequent, severe, or disrupts your sleep or confidence, it’s worth looking into.
With a few adjustments—or help from a doctor—you can likely reduce the issue and enjoy a more comfortable night’s sleep, minus the soggy pillow.