HT! These are the consequences of sleeping co! See more
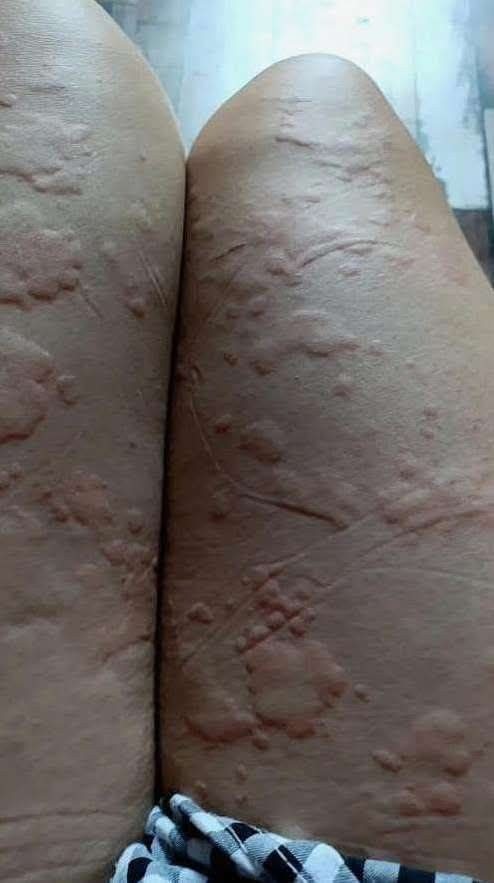
Noticing a bump or change in the genital area can feel uncomfortable and even alarming. Many people worry immediately about serious infections or long lasting conditions. While embarrassment often prevents open discussion, it is important to know that genital skin changes are very common. In many cases, they are harmless and easily treated once the cause is properly identified.
The skin in the genital area is especially sensitive. It is exposed to moisture, heat, friction, and constant movement, all of which can trigger irritation. Everyday factors such as shaving, waxing, tight clothing, sweating, or prolonged exercise can lead to temporary bumps, redness, or swelling. Minor cuts or ingrown hairs can also cause small lumps that usually improve on their own within a few days.
One of the most frequent causes of genital bumps is folliculitis. This condition occurs when hair follicles become inflamed or infected, often after shaving or when sweat and bacteria become trapped against the skin. Folliculitis typically appears as small red or white bumps that may itch, feel tender, or resemble pimples. Keeping the area clean, dry, and avoiding further irritation often allows the skin to heal. Persistent or painful cases may require medical treatment, such as topical or oral medications.
Sebaceous cysts are another common and usually harmless cause of genital lumps. These develop when oil glands become blocked, leading to a smooth, round bump beneath the skin. Sebaceous cysts usually grow slowly and are painless. They often require no treatment unless they become inflamed, infected, or uncomfortable. If a cyst becomes red, swollen, or painful, a healthcare provider should evaluate it to rule out infection and determine the best course of care.
Some genital bumps are related to infections and should always be medically assessed. Genital warts, caused by certain strains of human papillomavirus, often appear as small flesh colored or slightly raised growths. They may be flat or clustered and are usually painless. Although genital warts are not typically dangerous, diagnosis and treatment are important to manage symptoms and reduce the risk of spreading the virus to others.
The herpes simplex virus is another condition that can cause noticeable genital changes. Herpes often begins with tingling, burning, or itching, followed by the appearance of small fluid filled blisters. These blisters eventually break open and form sores before healing. While herpes is a lifelong infection, antiviral medications can significantly reduce the severity and duration of outbreaks and lower the risk of transmission.
Other infections may also cause genital lesions that are easy to miss. Molluscum contagiosum can cause small, firm bumps with a central indentation and is usually painless. Syphilis may present as a single painless sore in its early stage, which can heal on its own but still requires treatment to prevent serious complications. Because these conditions do not always cause discomfort, they can go unnoticed without careful attention.
Any genital change that is persistent, painful, spreading, recurring, or accompanied by other symptoms such as fever or unusual discharge should be checked by a healthcare provider. Early evaluation allows for accurate diagnosis and timely treatment, which can prevent complications and protect both personal and sexual health.
Genital health concerns are medical issues, not personal failures or sources of shame. Seeking care early provides reassurance, answers, and appropriate treatment. Paying attention to changes in your body and responding promptly supports overall health and peace of mind.