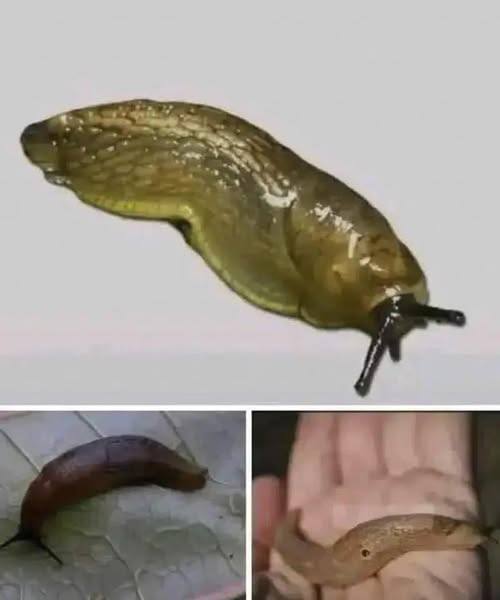
When a slug visits your house, it means you have…
Slugs, often dismissed as slimy garden pests, play a surprisingly important role in both nature and science. While their appearance might be unappealing to some, these humble creatures contribute much more than meets the eye. Beyond slowly creeping through gardens after rain, slugs help maintain ecological balance in meaningful ways.
In the natural world, slugs act as quiet recyclers. They feed on fallen leaves, fungi, and decaying plant material, aiding the decomposition process and returning vital nutrients to the soil. This enrichment boosts soil fertility and supports healthy plant growth, making slugs key players in sustaining ecosystems.
They are also an essential part of the food chain. Slugs serve as a critical food source for birds, toads, hedgehogs, beetles, and other animals. By supporting the diets of these predators, slugs help maintain biodiversity and balance within various habitats.
Interestingly, slug mucus has also caught the attention of researchers and developers. This sticky secretion is rich in regenerative, antibacterial, and anti-inflammatory properties. It shows potential in promoting wound healing and has begun to draw interest in the medical field.
In the beauty industry, slug slime is being studied for its similarities to snail mucus, which is already used in skincare for its hyaluronic acid and antioxidant content. These components are known to hydrate and protect skin, making slug-derived compounds a potential source for natural, effective skincare products.
Even in neuroscience, slugs have made a mark. Despite their simple nervous systems, they offer valuable insights into how memory and learning work. This makes them useful models for studying basic brain functions.
In summary, slugs may seem unremarkable at first glance, but their contributions—from nurturing the soil to advancing science—are impressive. They serve as a reminder that every organism, no matter how overlooked, has a role to play in the complex web of life.


![[VERY SAD] ‘The Price is Right’ long-time members SAYS GOODBYE and parted ways, host Drew Carey having an EMOTIONAL MOMENT](https://tinyhouse-zone.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/501623552_1033408738929086_3705169106047749628_n.jpg)